MACHINE LEARNING AND DEEP LEARNING-BASED APPROACHES ON VARIOUS BIOMARKERS FOR ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE EARLY DETECTION: A REVIEW
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.15282/ijsecs.7.2.2021.4.0087Keywords:
Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Deep Learning, Genetic variants, Machine learning, Mild cognitive impairment (MCI), Normal control (NC), Neuroimaging data, Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNPs)Abstract
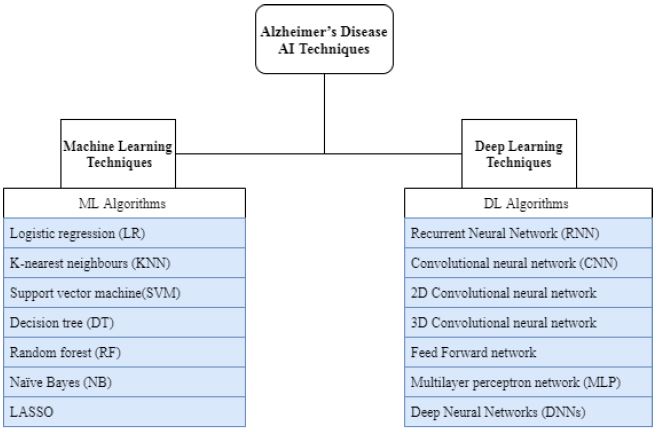
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder. It can cause a massive impact on a patient's memory and mobility. As this disease is irreversible, early diagnosis is crucial for delaying the symptoms and adjusting the patient's lifestyle. Many machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) based-approaches have been proposed to accurately predict AD before its symptoms onset. However, finding the most effective approach for AD early prediction is still challenging. This review explored 24 papers published from 2018 until 2021. These papers have proposed different approaches using state of the art machine learning and deep learning algorithms on different biomarkers to early detect AD. The review explored them from different perspectives to derive potential research gaps and draw conclusions and recommendations. It classified these recent approaches in terms of the learning technique used and AD biomarkers. It summarized and compared their findings, and defined their strengths and limitations. It also provided a summary of the common AD biomarkers. From this review, it was found that some approaches strove to increase the prediction accuracy regardless of their complexity such as using heterogeneous datasets, while others sought to find the most practical and affordable ways to predict the disease and yet achieve good accuracy such as using audio data. It was also noticed that DL based-approaches with image biomarkers remarkably surpassed ML based-approaches. However, they achieved poorly with genetic variants data. Despite the great importance of genetic variants biomarkers, their large variance and complexity could lead to a complex approach or poor accuracy. These data are crucial to discover the underlying structure of AD and detect it at early stages. However, an effective pre-processing approach is still needed to refine these data and employ them efficiently using the powerful DL algorithms.
References
“2020 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures,” Alzheimer’s Dement., vol. 16, no. 3, pp. 391–460, 2020, doi:
1002/alz.12068.
L. E. Hebert, J. Weuve, P. A. Scherr, and D. A. Evans, “Alzheimer disease in the US (2010-2050) estimated using
the 2010 census,” Neurology, vol. 80, no. 19, pp. 1778–1783, 2013.
K. G. Yiannopoulou and S. G. Papageorgiou, “Current and future treatments for Alzheimer’s disease,” Ther. Adv.
Neurol. Disord., vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 19–33, 2013, doi: 10.1177/1756285612461679.
P. Kishore, U. C. Kumari, M. N. V. S. S. Kumar, and T. Pavani, “Detection and analysis of Alzheimer’s disease
using various machine learning algorithms,” Mater. Today Proc., vol. 45, no. xxxx, pp. 1502–1508, 2021, doi:
1016/j.matpr.2020.07.645.
D. E. Barnes, and S. J. Lee, “Predicting Alzheimer’s risk: Why and how?,” Alzheimer’s Res. Ther., vol. 3, no. 6,
pp. 1–3, Nov. 2011, doi: 10.1186/alzrt95.
A. P. Porsteinsson, R. S. Isaacson, S. Knox, M. N. Sabbagh, and I. Rubino, “Diagnosis of Early Alzheimer’s
Disease: Clinical Practice in 2021,” J. Prev. Alzheimer’s Dis., 2021, doi: 10.14283/jpad.2021.23.
P. Ongsulee, “Artificial intelligence, machine learning and deep learning,” Int. Conf. ICT Knowl. Eng., pp. 1–6,
, doi: 10.1109/ICTKE.2017.8259629.
M. I. Jordan, and T. M. Mitchell, “Machine learning: Trends, perspectives, and prospects,” Science (80-. )., vol.
, no. 6245, 2015.
J. Qiu, Q. Wu, G. Ding, Y. Xu, and S. Feng, “A survey of machine learning for big data processing,” EURASIP
J. Adv. Signal Process., vol. 2016, no. 1, 2016, doi: 10.1186/s13634-016-0355-x.
N. K. Chauhan, and K. Singh, “A review on conventional machine learning vs deep learning,” 2018 Int. Conf.
Comput. Power Commun. Technol. GUCON 2018, pp. 347–352, 2019, doi: 10.1109/GUCON.2018.8675097.
S. Yang, J. M. S. Bornot, K. Wong-Lin, and G. Prasad, “M/EEG-Based Bio-Markers to Predict the MCI and
Alzheimer’s Disease: A Review from the ML Perspective,” IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng., vol. 66, no. 10, pp. 2924–
, 2019, doi: 10.1109/TBME.2019.2898871.
X. Wang, J. Qi, Y. Yang, and P. Yang, “A survey of disease progression modeling techniques for alzheimer’s
diseases,” IEEE Int. Conf. Ind. Informatics, vol. 2019-July, pp. 1237–1242, 2019, doi:
1109/INDIN41052.2019.8972091.
S. Grampurohit and C. Sagarnal, “Disease prediction using machine learning algorithms,” 2020 Int. Conf. Emerg.
Technol. INCET 2020, no. December, 2020, doi: 10.1109/INCET49848.2020.9154130.
T. Jo, K. Nho, and A. J. Saykin, “Deep Learning in Alzheimer’s Disease: Diagnostic Classification and Prognostic
Prediction Using Neuroimaging Data,” Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, vol. 11. 2019, doi:
3389/fnagi.2019.00220.
E. Lin, C.-H. Lin, and H.-Y. Lane, “Deep Learning with Neuroimaging and Genomics in Alzheimer’s Disease,”
Int. J. Mol. Sci., vol. 22, no. 15, p. 7911, 2021, doi: 10.3390/ijms22157911.
J. De Velasco Oriol, E. E. Vallejo, K. Estrada, J. G. Taméz Peña, and T. A. s. Disease Neuroimaging Initiative,
“Benchmarking machine learning models for late-onset Alzheimer’s disease prediction from genomic data,” BMC
Bioinformatics, vol. 20, no. 1, p. 709, Dec. 2019, doi: 10.1186/s12859-019-3158-x.
J. Zhou, L. Hu, Y. Jiang, and L. Liu, “A Correlation Analysis between SNPs and ROIs of Alzheimer’s Disease
Based on Deep Learning,” Biomed Res. Int., vol. 2021, 2021, doi: 10.1155/2021/8890513.
Q. Ying, X. Xing, G. Liang, and I. City, “Multi-Modal Data Analysis for Alzheimer ’ s Disease Diagnosis : An
Ensemble Model Using Imagery and Genetic Features,” bioRxiv, pp. 5–10, 2021.
K. Ning et al., “Classifying Alzheimer’s disease with brain imaging and genetic data using a neural network
framework,” Neurobiol. Aging, vol. 68, pp. 151–158, 2018, doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2018.04.009.
J. Williamson, J. Goldman, and K. S. Marder, “Genetic aspects of alzheimer disease,” Neurologist, vol. 15, no.
pp. 80–86, Mar. 2009, doi: 10.1097/NRL.0b013e318187e76b.
Q. Sun, N. Xie, B. Tang, R. Li, and Y. Shen, “Alzheimer’s disease: From genetic variants to the distinct
pathological mechanisms,” Front. Mol. Neurosci., vol. 10, no. October, pp. 1–14, 2017, doi:
3389/fnmol.2017.00319.
R. Mishra, and B. Li, “The application of artificial intelligence in the genetic study of Alzheimer’s disease,” Aging
Dis., vol. 11, no. 6, pp. 1567–1584, 2020, doi: 10.14336/AD.2020.0312.
A. T. Isik, “Late onset Alzheimer’s disease in older people.,” Clin. Interv. Aging, vol. 5, pp. 307–311, 2010, doi:
2147/cia.s11718.
S. Behjati and P. S. Tarpey, “What is next generation sequencing?,” Arch. Dis. Child. Educ. Pract. Ed., vol. 98,
no. 6, pp. 236–238, Dec. 2013, doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2013-304340.
A. L. Tarca, R. Romero, and S. Draghici, “Analysis of microarray experiments of gene expression profiling,”
doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2006.07.001.
G. Novelli, C. Ciccacci, P. Borgiani, M. P. Amati, and E. Abadie, “Genetic tests and genomic biomarkers:
Regulation, qualification and validation,” 2008.
D. S. W. Ho, W. Schierding, M. Wake, R. Saffery, and J. O’Sullivan, “Machine learning SNP based prediction
for precision medicine,” Frontiers in Genetics, vol. 10, no. MAR. Frontiers Media S.A., 2019, doi:
3389/fgene.2019.00267.
S. Uddin, A. Khan, M. E. Hossain, and M. A. Moni, “Comparing different supervised machine learning
algorithms for disease prediction,” BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak., vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 1–16, 2019, doi:
1186/s12911-019-1004-8.
R. Tarawneh, “Biomarkers: Our Path Towards a Cure for Alzheimer Disease,” Biomark. Insights, vol. 15, 2020,
doi: 10.1177/1177271920976367.
S. Lovestone, “Biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease,” Res. Pract. Alzheimers. Dis., vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 41–50, Mar.
, doi: 10.1515/almed-2020-0090.
W. M. van Oostveen and E. C. M. de Lange, “Imaging techniques in alzheimer’s disease: A review of applications
in early diagnosis and longitudinal monitoring,” Int. J. Mol. Sci., vol. 22, no. 4, pp. 1–34, 2021, doi:
3390/ijms22042110.
G. Gifford, R. McCutcheon, and P. McGuire, “Neuroimaging studies in people at clinical high risk for psychosis,”
Risk Factors Psychos., pp. 167–182, Jan. 2020, doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-813201-2.00009-0.
S. Al-Shoukry, T. H. Rassem, and N. M. Makbol, “Alzheimer’s diseases detection by using deep learning
algorithms: A mini-review,” IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 77131–77141, 2020, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2989396.
G. S. Bloom, “Amyloid-β and tau: The trigger and bullet in Alzheimer disease pathogenesis,” JAMA Neurol., vol.
, no. 4, pp. 505–508, 2014, doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2013.5847.
P. A. Rowley, A. A. Samsonov, T. J. Betthauser, A. Pirasteh, S. C. Johnson, and L. B. Eisenmenger, “Amyloid
and Tau PET Imaging of Alzheimer Disease and Other Neurodegenerative Conditions,” Semin. Ultrasound, CT
MRI, vol. 41, no. 6, pp. 572–583, Dec. 2020, doi: 10.1053/j.sult.2020.08.011.
A. J. Saykin et al., “Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative biomarkers as quantitative phenotypes:
Genetics core aims, progress, and plans,” Alzheimer’s Dement., vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 265–273, 2010, doi:
1016/j.jalz.2010.03.013.
D. S. Marcus, T. H. Wang, J. Parker, J. G. Csernansky, J. C. Morris, and R. L. Buckner, “Open Access Series of
Imaging Studies (OASIS): Cross-sectional MRI data in young, middle aged, nondemented, and demented older
adults,” J. Cogn. Neurosci., vol. 19, no. 9, pp. 1498–1507, Sep. 2007, doi: 10.1162/jocn.2007.19.9.1498.
J. Tian et al., “Modular machine learning for Alzheimer’s disease classification from retinal vasculature,” Sci.
Rep., vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 1–11, 2021, doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-80312-2.
P. J. Snyder et al., “Retinal imaging in Alzheimer’s and neurodegenerative diseases,” Alzheimer’s Dement., vol.
, no. 1, pp. 103–111, 2021, doi: 10.1002/alz.12179.
C. Sudlow et al., “UK Biobank: An Open Access Resource for Identifying the Causes of a Wide Range of
Complex Diseases of Middle and Old Age,” PLoS Med., vol. 12, no. 3, Mar. 2015, doi:
1371/journal.pmed.1001779.
F. E. K. Al-Khuzaie, O. Bayat, and A. D. Duru, “Diagnosis of Alzheimer Disease Using 2D MRI Slices by
Convolutional Neural Network,” Appl. Bionics Biomech., vol. 2021, 2021, doi: 10.1155/2021/6690539.
M. L. Metzker, “Sequencing technologies the next generation,” Nat. Rev. Genet., vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 31–46, 2010,
doi: 10.1038/nrg2626.
W. S. Bush and J. H. Moore, “Chapter 11: Genome-Wide Association Studies,” PLoS Comput. Biol., vol. 8, no.
, 2012, doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002822.
C. S. Ku, E. Y. Loy, A. Salim, Y. Pawitan, and K. S. Chia, “The discovery of human genetic variations and their
use as disease markers: Past, present and future,” J. Hum. Genet., vol. 55, no. 7, pp. 403–415, 2010, doi:
1038/jhg.2010.55.
A. Anjum, S. Jaggi, E. Varghese, S. Lall, A. Bhowmik, and A. Rai, “Identification of Differentially Expressed
Genes in RNA-seq Data of Arabidopsis thaliana: A Compound Distribution Approach,” J. Comput. Biol., vol.
, no. 4, pp. 239–247, 2016, doi: 10.1089/cmb.2015.0205.
S. Perera, K. Hewage, C. Gunarathne, R. Navarathna, D. Herath, and R. G. Ragel, “Detection of Novel Biomarker
Genes of Alzheimer’s Disease Using Gene Expression Data,” MERCon 2020 - 6th Int. Multidiscip. Moratuwa
Eng. Res. Conf. Proc., pp. 1–6, 2020, doi: 10.1109/MERCon50084.2020.9185336.
J. F. Loring, X. Wen, J. M. Lee, J. Seilhamer, and R. Somogyi, “A gene expression profile of Alzheimer’s
disease,” DNA Cell Biol., vol. 20, no. 11, pp. 683–695, 2001, doi: 10.1089/10445490152717541.
P. Danecek et al., “The variant call format and VCFtools,” Bioinformatics, vol. 27, no. 15, pp. 2156–2158, Aug.
, doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr330.
L. Liu, S. Zhao, H. Chen, and A. Wang, “A new machine learning method for identifying Alzheimer’s disease,”
Simul. Model. Pract. Theory, vol. 99, p. 102023, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.simpat.2019.102023.
B. Ghoraani, L. N. Boettcher, M. D. Hssayeni, A. Rosenfeld, M. I. Tolea, and J. E. Galvin, “Detection of mild
cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease using dual-task gait assessments and machine learning,” Biomed.
Signal Process. Control, vol. 64, no. August 2020, p. 102249, 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2020.102249.
A. Khan, and S. Zubair, “An Improved Multi-Modal based Machine Learning Approach for the Prognosis of
Alzheimer’s disease,” J. King Saud Univ. - Comput. Inf. Sci., no. xxxx, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.jksuci.2020.04.004.
Y. Zheng, H. Guo, L. Zhang, J. Wu, Q. Li, and F. Lv, “Machine learning-based framework for differential
diagnosis between vascular dementia and Alzheimer’s disease using structural mri features,” Front. Neurol., vol.
, no. OCT, pp. 1–9, 2019, doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.01097.
V. P. S. Rallabandi, K. Tulpule, and M. Gattu, “Automatic classification of cognitively normal, mild cognitive
impairment and Alzheimer’s disease using structural MRI analysis,” Informatics Med. Unlocked, vol. 18, 2020,
doi: 10.1016/j.imu.2020.100305.
J. H. Park et al., “Machine learning prediction of incidence of Alzheimer’s disease using large-scale
administrative health data,” npj Digit. Med., vol. 3, no. 1, 2020, doi: 10.1038/s41746-020-0256-0.
M. Grassi et al., “A novel ensemble-based machine learning algorithm to predict the conversion from mild
cognitive impairment to Alzheimer’s disease using socio-demographic characteristics, clinical information, and
neuropsychological measures,” Front. Neurol., vol. 10, no. JUL, pp. 1–15, 2019, doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00756.
N. Arzouni, W. Matloff, L. Zhao, K. Ning, and A. W. Toga, “Identification of Dysregulated Genes for Late-Onset
Alzheimer’s Disease Using Gene Expression Data in Brain.,” J. Alzheimer’s Dis. Park., vol. 10, no. 6, 2020,
[Online]. Available:
=PMC7717689.
B. L. Romero-Rosales, J. G. Tamez-Pena, H. Nicolini, M. G. Moreno-Treviño, and V. Trevino, “Improving
predictive models for Alzheimer’s disease using GWAS data by incorporating misclassified samples modeling,”
PLoS One, vol. 15, no. 4, pp. 1–15, 2020, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0232103.
U. Rangaswamy, S. A. P. Dharshini, D. Yesudhas, and M. M. Gromiha, “VEPAD - Predicting the effect of
variants associated with Alzheimer’s disease using machine learning,” Comput. Biol. Med., vol. 124, no. August,
p. 103933, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2020.103933.
S. Katabathula, Q. Wang, and R. Xu, “Predict Alzheimer’s disease using hippocampus MRI data: a lightweight
D deep convolutional network model with visual and global shape representations,” Alzheimer’s Res. Ther., vol.
, no. 1, pp. 1–9, 2021, doi: 10.1186/s13195-021-00837-0.
T. Jo, K. Nho, S. L. Risacher, and A. J. Saykin, “Deep learning detection of informative features in tau PET for
Alzheimer’s disease classification,” BMC Bioinformatics, vol. 21, no. 21, pp. 1–14, 2020, doi: 10.1186/s12859-
-03848-0.
A. Punjabi, A. Martersteck, Y. Wang, T. B. Parrish, and A. K. Katsaggelos, “Neuroimaging modality fusion in
Alzheimer’s classification using convolutional neural networks,” PLoS One, vol. 14, no. 12, pp. 1–14, 2019, doi:
1371/journal.pone.0225759.
V. S. Nori, C. A. Hane, Y. Sun, W. H. Crown, and P. A. Bleicher, “Deep neural network models for identifying
incident dementia using claims and EHR datasets,” PLoS One, vol. 15, no. 9 September, pp. 1–12, 2020, doi:
1371/journal.pone.0236400.
J. de Velasco Oriol, E. Vallejo, and K. Estrada, “Predicting late-onset Alzheimer’s disease from genomic data
using deep neural networks,” bioRxiv, p. 629402, 2019, doi: 10.1101/629402.
W. J. Lim, K. H. Kim, J. Y. Kim, S. Jeong, and N. Kim, “Identification of DNA-methylated CpG islands
associated with gene silencing in the adult body tissues of the ogye chicken using RNA-Seq and reduced
representation bisulfite sequencing,” Front. Genet., vol. 10, no. APR, p. 346, 2019, doi:
3389/fgene.2019.00346.
C. Park, J. Ha, and S. Park, “Prediction of Alzheimer’s disease based on deep neural network by integrating gene
expression and DNA methylation dataset,” Expert Syst. Appl., vol. 140, p. 112873, 2020, doi:
1016/j.eswa.2019.112873.
S. Mishra, A. Dash, and L. Jena, “Use of deep learning for disease detection and diagnosis,” in Studies in
Computational Intelligence, vol. 903, Springer, 2021, pp. 181–201.
L. Koumakis, “Deep learning models in genomics; are we there yet?,” Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J., vol. 18, pp.
–1473, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2020.06.017.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2021 Ghada Alqubati, Ghaleb Algaphari

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






